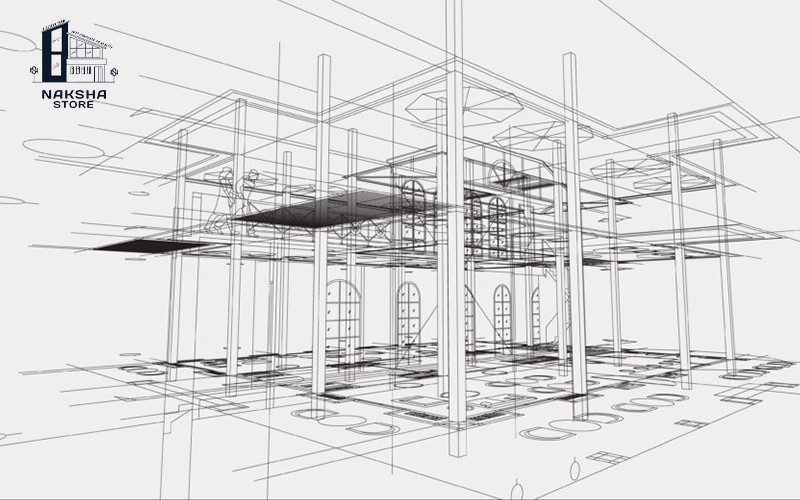
Structure design refers to the process of designing the framework and support system of a building or structure to ensure its stability, safety, and structural integrity. It involves the application of engineering principles, analysis, and calculations to determine the appropriate materials, dimensions, and construction methods for the structural elements. Here are some key aspects and considerations in structure design:
Load Analysis: The first step in structure design is to analyze and determine the various types of loads that the structure will be subjected to, such as dead loads (the weight of the structure itself), live loads (occupancy and usage), wind loads, seismic loads, and snow loads. Understanding the magnitude and distribution of these loads is essential for designing the appropriate structural elements.
Structural System: The structural system refers to the arrangement and configuration of the load-bearing elements within the building. It can be classified into various types such as beams, columns, slabs, walls, frames, trusses, or a combination of these. The choice of structural system depends on factors such as architectural requirements, span lengths, load distribution, and construction constraints.
Material Selection: The selection of materials for the structural elements is critical to ensure strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Common structural materials include concrete, steel, timber, masonry, and composite materials. The choice of material depends on factors such as the structural requirements, local availability, environmental conditions, and cost considerations.
Structural Analysis: Structural analysis involves performing calculations and simulations to determine the forces, stresses, and deformations that the structure will experience under different load conditions. This analysis helps ensure that the structural elements can safely resist the applied loads and that any deflections or deformations are within acceptable limits.
Foundation Design: The design of the foundation is crucial for transferring the loads from the structure to the underlying soil or rock. The foundation must be designed to bear the weight of the structure and to resist movements caused by soil settlement or external forces. Factors such as soil conditions, site characteristics, and the structural loads influence the type and design of the foundation system.
Seismic Design: In areas prone to earthquakes, the structure must be designed to withstand seismic forces. Seismic design involves considering factors such as the site's seismic hazard, soil conditions, and the building's response to ground motion. Techniques such as base isolation, damping systems, and reinforced concrete shear walls are employed to enhance the structure's seismic performance.
Structural Connections: Proper design of structural connections is crucial for ensuring the integrity and stability of the overall structure. Connections between beams, columns, walls, and other elements must be designed to transmit forces effectively and safely while considering factors such as material compatibility, load transfer, and constructability.
Building Codes and Regulations: Structure design must adhere to local building codes and regulations that define the minimum standards for safety and structural performance. These codes specify requirements related to material strength, structural design criteria, load limits, fire safety, and other considerations.
The ultimate goal of structure design is to create a safe, durable, and efficient building or structure that can withstand the applied loads and environmental forces throughout its intended lifespan. Collaboration between architects, structural engineers, and other professionals is crucial to ensure a successful and well-integrated structure design.